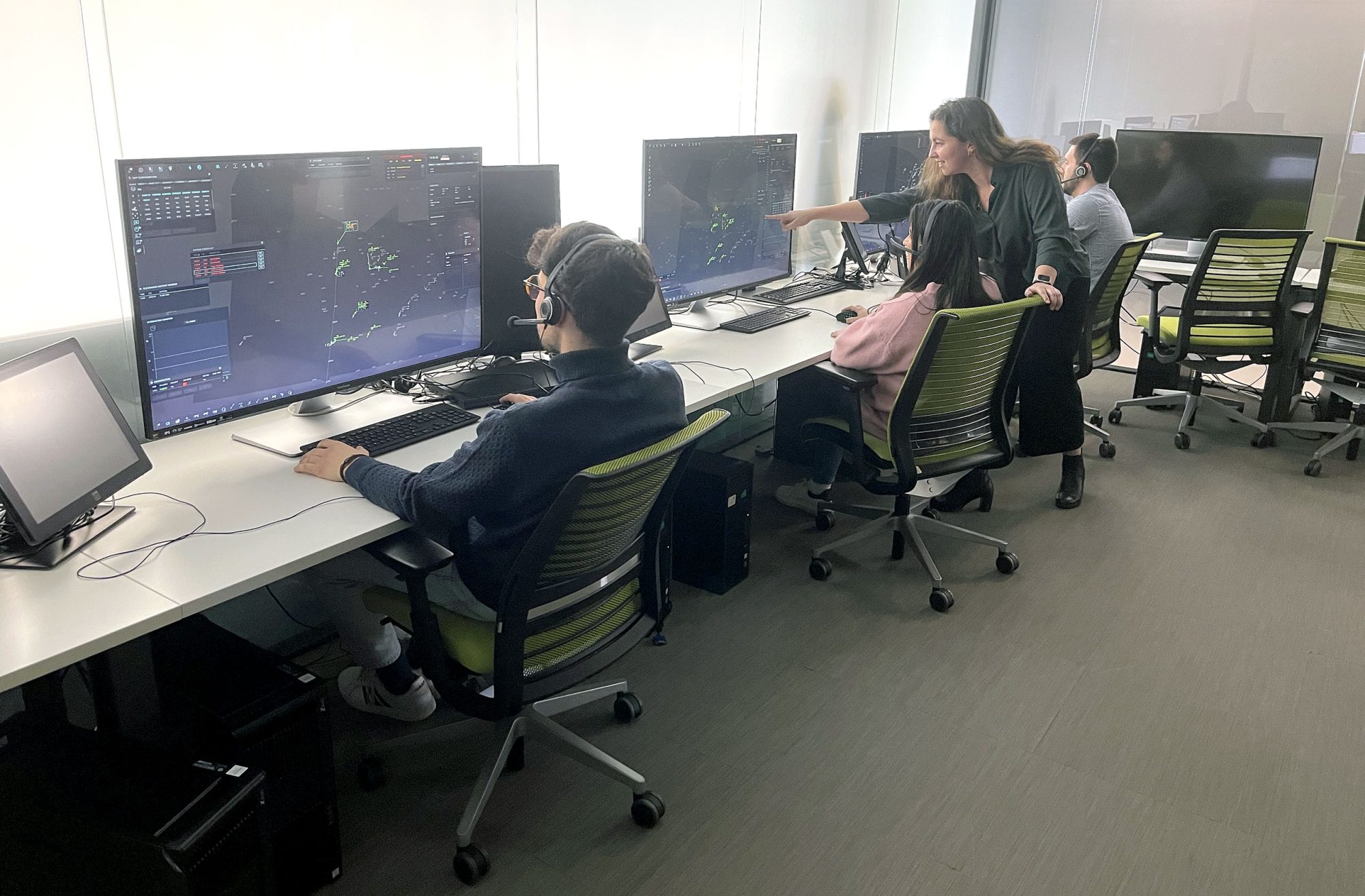
Exercise 002, led by ENAIRE, is a high-fidelity real-time simulation focused on assessing the operational feasibility and benefits of the FCA concept in Spanish upper airspace. The validated scenario will feature an FCA area within Madrid ACC’s upper airspace above flight level FL365. Depending on traffic density and complexity, 1 to 3 air traffic controllers are expected to operate in this FCA area.
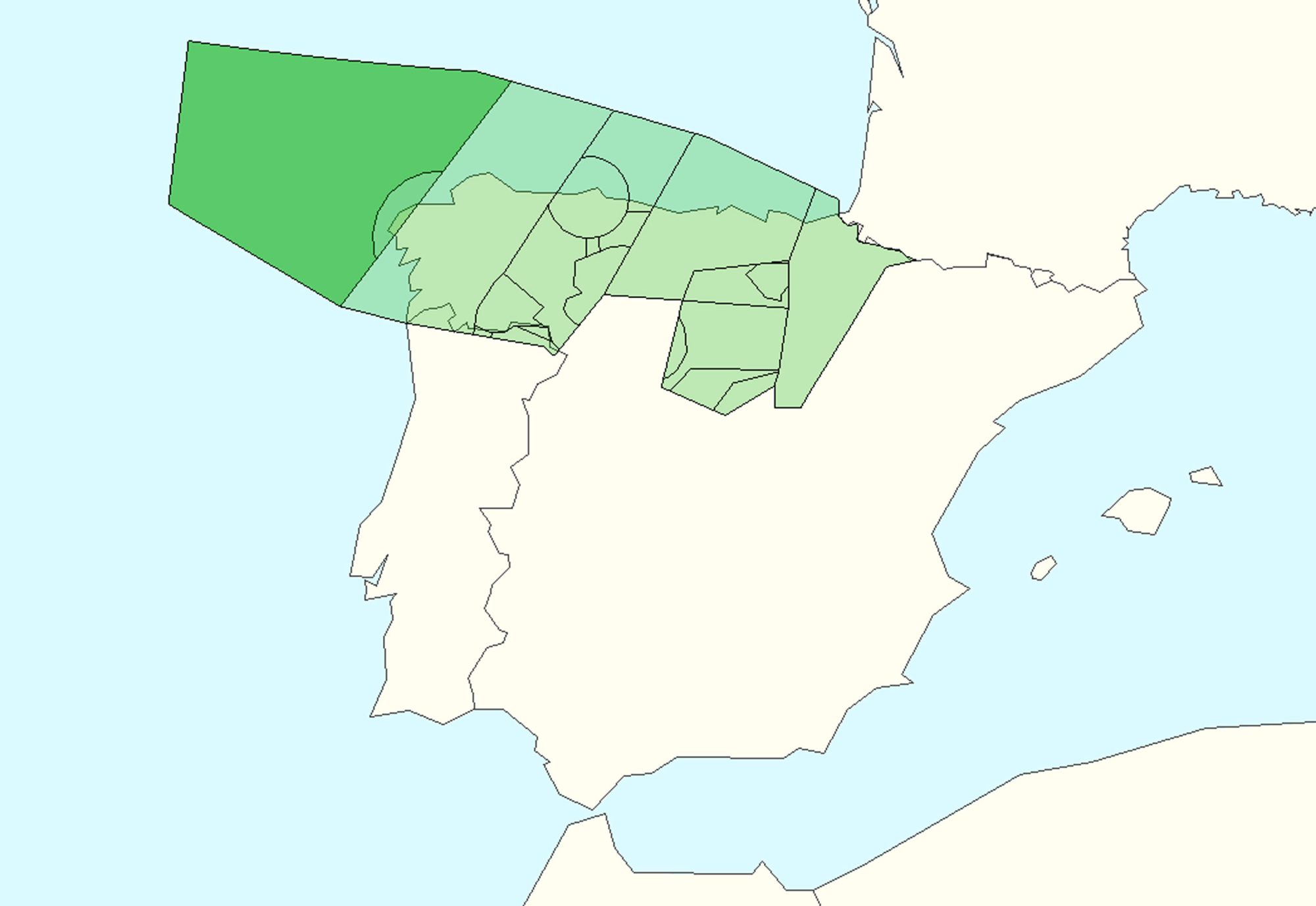
The exercise will evaluate tasks, roles, and responsibilities under both nominal and non-nominal conditions, with a particular emphasis on assessing the opening and closure of FCA positions, traffic allocation based on complexity, conflict resolution in FCA operations, and communications.
To manage varying traffic situations in the selected airspace, an Airstreams operating method will be introduced during high traffic density periods. This method integrates a significant portion of traffic into flows to simplify traffic within the FCA area and reduce the communication burden on ATC controllers. Flights within airstreams will be managed by a new type of ATCo, the Airstream Manager.
Validation will take place at the CRIDA experimental Centre in Madrid, Spain, from 24 March to 4 April 2025. Up to 11 ENAIRE air traffic controllers will participate in the simulations, acting in various roles to provide a comprehensive view of FCA area operations. Based on the scenario results, INECO will lead a complete safety assessment to ensure the concept’s safety performance.
The validations will be run in the ATC pre-operational iTEC platform. INDRA will enhance the iTEC platform and its HMI to support FCA operations, including the development of advanced functionalities for conflict detection and resolution tools. Additionally, a prototype named PUZZLE, developed by CRIDA, will assist in traffic allocation to FCA controllers by predicting and analysing complexity for each controller.
CRIDA will lead the preparation, execution and analysis of the overall exercise results and conduct complementary studies such as statistical analyses to identify optimal periods for opening or closing positions through simulated DCB processes. Exercise 2 will provide expected benefits of the concept in terms of safety, cost-efficiency, operational efficiency, environment, and human performance.
